Understanding ACES and PIES Data: A Comprehensive Guide for the Automotive Aftermarket Industry

In the fast-paced world of the automotive aftermarket, precision and efficiency are keys to success.
Enter ACES (Aftermarket Catalog Exchange Standard) and PIES (Product Information Exchange Standard) – the cornerstone data standards developed by the Auto Care Association.
These standards revolutionize how manufacturers, distributors, and retailers manage and exchange vehicle fitment and product information. By standardizing data across the supply chain, ACES and PIES ensure unparalleled accuracy and consistency, driving better business outcomes and enhancing customer satisfaction.
Dive into this comprehensive guide to master the intricacies of ACES and PIES and take your automotive aftermarket operations to the next level.
What are ACES & PIES?
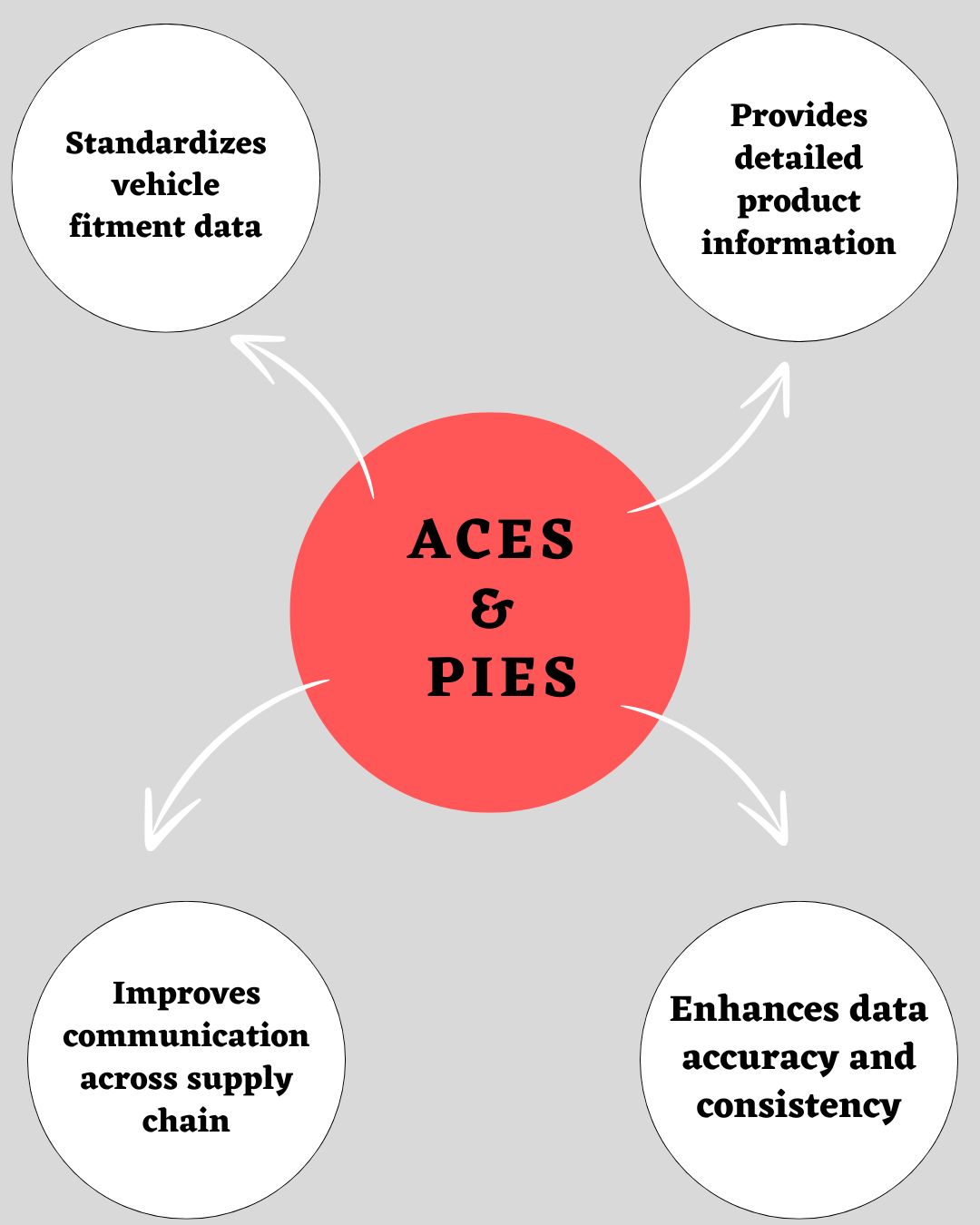
ACES (Aftermarket Catalog Exchange Standard) and PIES (Product Information Exchange Standard) are data standards that were created by the Auto Care Association, a leading industry organization dedicated to supporting the automotive aftermarket.
Their goal was to improve data accuracy, consistency, and communication across the supply chain, benefiting manufacturers, distributors, retailers, and, ultimately, consumers.
- ACES provides a standardized format for managing and exchanging vehicle fitment data, ensuring accuracy and consistency for parts applications across various vehicle makes, models, and years.
- PIES offers a standardized format for sharing more detailed product information, including specifications, pricing, packaging, and more.
Together, ACES and PIES standards streamline operations, reduce errors, and enhance the accuracy and reliability of automotive parts data across the supply chain.
Coverage Years of ACES and PIES Data
Vehicle Coverage Periods for ACES
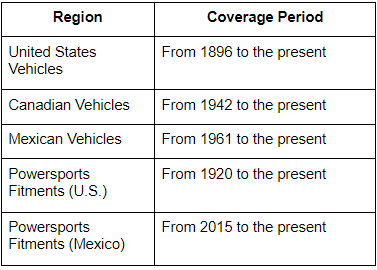
Vehicle Coverage Periods for PIES
What ACES and PIES Does Not Include
Universal Parts without Specific Fitment
ACES and PIES do not include data for universal parts that do not have a specific vehicle fitment. These parts can be used across various vehicles without specific compatibility requirements, and these standards do not cover them.
Example: Items like generic car accessories, cleaning products, or universal tools.
Proprietary Product Information
ACES and PIES standards focus on standardized data specifications that can be universally applied across the automotive aftermarket industry. They do not include proprietary information specific to a single manufacturer or retailer that is not meant for public exchange.
Note: Brand owners can add custom product attributes to describe unique features or specifications that are not covered by the standard ACES attributes. This can include proprietary technologies, special materials, or unique design elements.
Example: Proprietary performance data, unique branding details, or confidential design specifications.
Custom or Modified Vehicle Data
Data for custom-built or heavily modified vehicles, which do not conform to standard vehicle configurations, are not included in ACES and PIES. These vehicles often require unique parts and configurations that fall outside the scope of standardized data.
Example: Custom hot rods, modified off-road vehicles, or one-of-a-kind show cars.
In-depth Technical Repair Procedures
ACES and PIES provide information on parts and fitment but do not include detailed technical repair procedures or service manuals.
Example: Step-by-step instructions for repairing or replacing a specific part.
Historical Data Beyond Coverage
While ACES and PIES cover a wide range of vehicles dating back many years, they do not include historical data for vehicles that fall outside their defined coverage periods.
Example: Vehicles older than the specified coverage years, such as pre-1896 U.S. vehicles or pre-1942 Canadian vehicles.
Non-Automotive Products
Products not related to the automotive, powersports, or heavy-duty vehicle industries are not included in ACES and PIES standards.
Example: Household appliances, consumer electronics, or non-automotive machinery.
Who Maintains ACES and PIES Data?

Today, the Auto Care Association and their Technology Standards Committee (TSC) play a pivotal role in managing the ACES and PIES data.
Responsibilities of the Auto Care Association
- Maintenance and Updates: The Auto Care Association is tasked with the ongoing maintenance of both ACES and PIES. This includes regular updates to reflect new vehicle models, changes in product information, and advancements in automotive technology.
- Standardization: The association ensures that ACES and PIES data adhere to established standards, promoting consistency and interoperability across the automotive aftermarket industry.
- Version Control: They manage version releases, incorporating feedback and making necessary revisions to keep the standards aligned with industry needs.
Role of the Technology Standards Committee (TSC)
- Guidance and Oversight: The TSC provides strategic direction and oversight for the development and evolution of ACES and PIES standards. This committee is composed of industry experts who bring a wealth of knowledge and experience to the table.
- Review and Approval: The TSC reviews proposed changes and updates to the standards, ensuring they meet industry requirements and address emerging trends and challenges.
- Coordination with Stakeholders: The committee collaborates with various stakeholders, including manufacturers, distributors, and retailers, to gather input and ensure that the standards meet the practical needs of all parties involved.
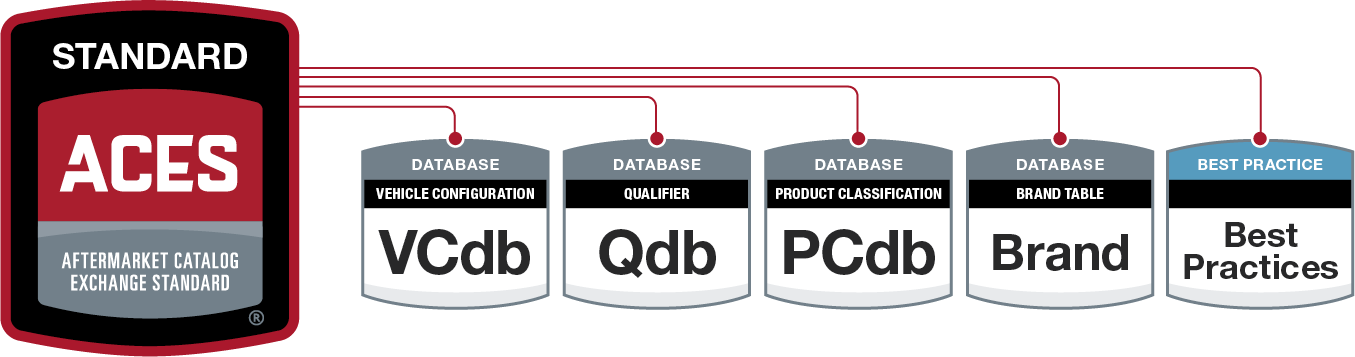
ACES (Aftermarket Catalog Exchange Standard)
ACES stands as the backbone of data management in the automotive aftermarket.
This standard allows aftermarket manufacturers to exchange parts data seamlessly using industry-standard vehicle applications. The data includes crucial details such as the year, make, model, part types, and qualifier statements, ensuring that every piece of information is uniform and easily interpretable across the supply chain.
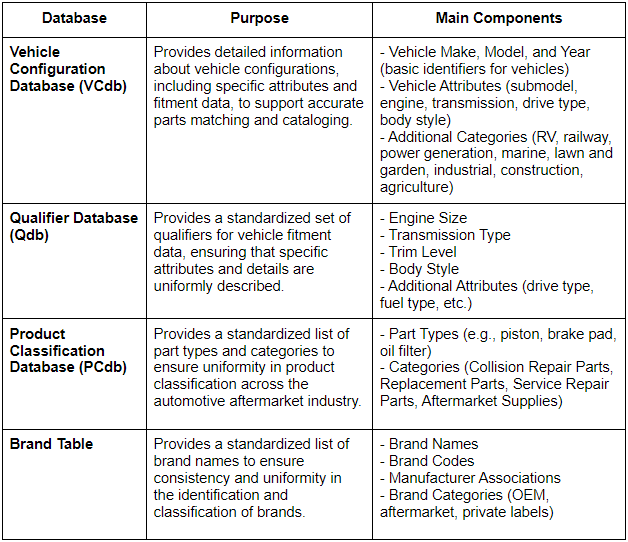
Key Components of ACES Data
ACES data includes essential information about each part, providing both basic and detailed application fitment information to ensure accurate compatibility with specific vehicles.
The key components of ACES data are:
- Brand: The manufacturer or brand name of the part.
- Part Number: A unique identifier for the part.
- Part Type: The category or type of part (e.g., brake pads, filters).
- AAIA Brand ID: Unique identifier for each brand to ensure consistency.
- Market Coverage: Geographical or market-specific information indicating where the part or vehicle is applicable
In addition to these basic details, ACES data also provides other information, which is crucial for determining vehicle compatibility:
- Vehicle Make, Model, and Year: Basic identifiers of the vehicle.
- Submodel, Engine, Transmission: Additional attributes that specify the exact fitment, ensuring the part matches specific configurations.
- Position: Information about the position of the part on the vehicle (e.g., front, rear, left, right)
- Fitment Notes: Additional notes or special instructions about part fitment.
- Other Attributes: Additional details such as truck bed length, drive type, and other specific vehicle attributes that further refine fitment accuracy.
- Interchange Data: Cross-references to other part numbers or alternative parts.
ACES Data Formats and Usage
ACES data is available in two primary formats: XML and JSON (JavaScript Object Notation).
These formats are widely used in the industry and allow for easy integration with various systems and platforms.
ACES Databases
PIES (Product Information Exchange Standard)
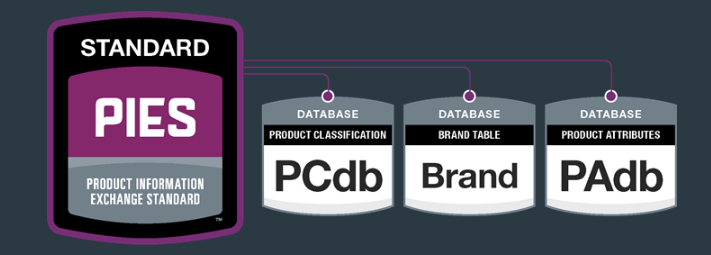
PIES, or Product Information Exchange Standard, focuses on more detailed information about products, such as specifications, pricing, and packaging.
This information allows manufacturers to establish rich, marketing-friendly product information that be used across multiple eCommerce platforms.
Key Components of PIES Data
PIES data includes essential information about each product:
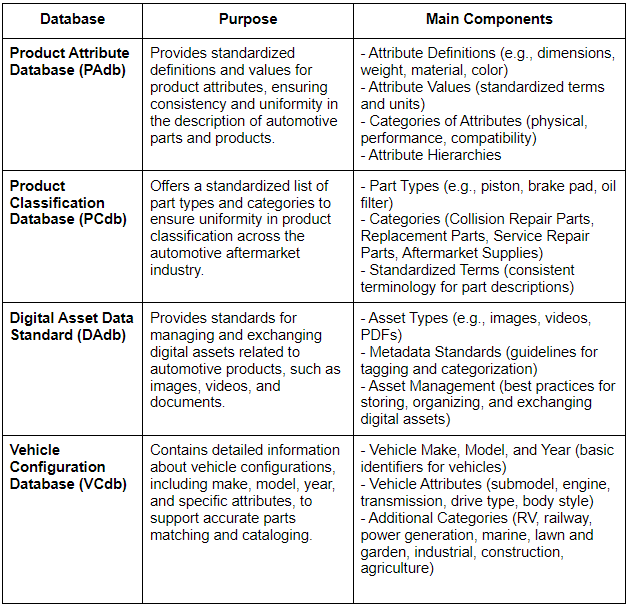
- Product Attributes: Detailed descriptions and values for product attributes such as dimensions, weight, material, color, and other specific characteristics.
- Product Categories: Standardized classification of parts into categories such as collision repair parts, replacement parts, service repair parts, and aftermarket supplies.
PIES Databases
Benefits of Using ACES & PIES
Streamlined Operations and Workflow
ACES and PIES provide standardized formats for data exchange, which significantly streamline operations and workflow. By ensuring that all data adheres to these standards, businesses can automate many processes, reduce manual data entry, and minimize errors.
Improved Customer Satisfaction
Accurate and consistent data from ACES and PIES leads to better product listings and more reliable parts matching. This accuracy reduces the chances of shipping incorrect parts, leading to higher customer satisfaction and fewer returns.
Enhanced Compatibility with E-commerce Platforms
ACES and PIES standards are widely recognized and supported by many e-commerce platforms. Using these standards ensures that your data is compatible with various platforms, facilitating seamless integration and enhancing your online presence.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Misunderstanding Data Requirements
One of the most common mistakes is not fully understanding the data requirements for ACES and PIES. This can lead to incomplete or inaccurate data submissions, which can cause issues down the line.
How to Avoid:
- Educate Your Team: Ensure that everyone involved in data management understands the specific requirements for ACES and PIES.
- Utilize Training Resources: Take advantage of training materials and resources provided by the Auto Care Association.
- Consult Guidelines: Regularly refer to the official guidelines and documentation for ACES and PIES.
Overlooking Data Quality Control
Neglecting data quality control can result in incorrect or inconsistent data, which can impact the reliability of parts matching and product information.
How to Avoid:
- Implement Quality Control Processes: Establish robust data quality control processes to check for accuracy and consistency.
- Use Validation Tools: Utilize data validation tools to automatically check for errors and inconsistencies in your data.
- Regular Audits: Conduct regular audits of your data to identify and correct any issues promptly.
Not Keeping Up with Updates
Failing to keep up with updates to the ACES and PIES standards can result in outdated data, which can lead to compatibility issues and inefficiencies.
How to Avoid:
- Stay Informed: Subscribe to updates from the Auto Care Association to stay informed about changes and new releases.
- Regular Reviews: Schedule regular reviews of your data and processes to ensure they are aligned with the latest standards.
- Engage with the Community: Participate in industry forums and discussions to stay current with best practices and updates.
FAQs on ACES & PIES
What are ACES and PIES?
ACES (Aftermarket Catalog Exchange Standard) and PIES (Product Information Exchange Standard) are data standards developed by the Auto Care Association to ensure consistent and accurate exchange of vehicle fitment and product information in the automotive aftermarket industry. They help streamline data management and improve the accuracy of product listings.
Why are ACES and PIES important for my business?
ACES and PIES help streamline operations by standardizing data formats, reducing errors, and improving the accuracy of product listings. This leads to enhanced compatibility with e-commerce platforms, better customer satisfaction, and more efficient workflows.
How do I get started with ACES and PIES?
To get started, you need the right tools and resources, including data management software that supports ACES and PIES standards, training materials, and validation tools. It’s also essential to choose the right software and service providers and involve your team in the implementation process. Implementing a robust Product Information Management (PIM) system can also facilitate the efficient handling of ACES and PIES data.
What is the Vehicle Configuration Database (VCdb)?
The VCdb is a component of ACES that provides detailed information about vehicle configurations, including make, model, year, and specific attributes such as submodel, engine, transmission, drive type, and body style. It supports accurate parts matching and cataloging.
How often are ACES and PIES data updated?
ACES and PIES data are regularly updated to include new vehicle models, changes in product information, and advancements in automotive technology. The Auto Care Association provides monthly updates to the Vehicle Configuration Database (VCdb) and other related databases. Using a PIM system can help keep your data current by integrating these updates seamlessly.
What tools and resources are needed for implementing ACES and PIES?
You need data management software that supports ACES and PIES, training materials to educate your team, and validation tools to ensure data compliance. Implementing a Product Information Management (PIM) system can greatly enhance your ability to manage and update product information accurately. It’s also beneficial to have access to the latest guidelines and documentation from the Auto Care Association.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when using ACES and PIES?
Common mistakes include misunderstanding data requirements, overlooking data quality control, and not keeping up with updates. To avoid these, ensure thorough education and training for your team, implement robust quality control processes, and stay informed about the latest updates and guidelines from the Auto Care Association.
Utilizing a PIM system can help manage data quality and streamline updates, reducing the risk of errors.
Ready to Make ACES and PIES Data Work For You?